Spring MVC 源码初探
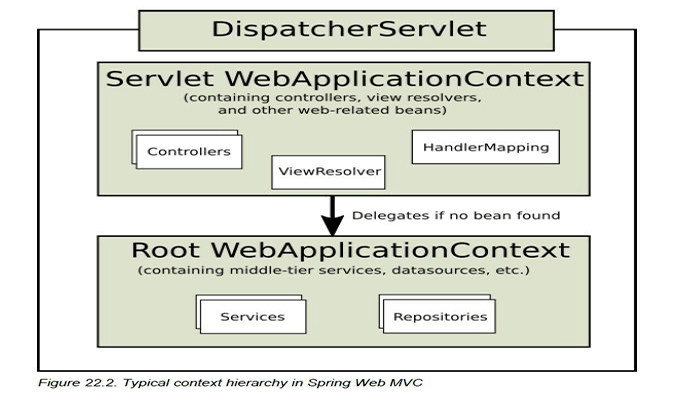
Servlet 3.0,可以支持 Java 配置的方式。关于源码的部分就尝试用注解的方式分析,感觉内部的逻辑因该是没有啥变化吧。关于 Spring MVC 相关的文档我有翻译过一个 Part VI. The Web,也可以到 github 下载。
在 Servlet3.0 中,容器会在类路径下查找 javax.servlet.ServletContainerInitializer 接口的实现类来配置 Servlet 的容器,在 Spring 中这个实现类是 SpringServletContainerInitializer。SpringServletContainerInitializer 这个类又会反过来查找实现了 WebApplicationInitializer 的类。
SpringMvcInitializer
1 |
|
上面 SpringMvcInitializer 类通过这样简单的方式就初始化了一个 web 容器。没错这样一个基础的 Spring MVC 项目就可以跑起来了。看一下此时的类图:
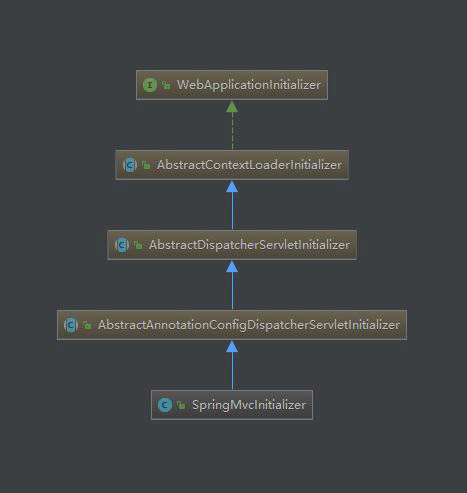
从这个图看来跟 xml 中需要配置的 listener 和 DispatcherServlet 也是很有关系。因为 class 加载机制,我们先从父类开始。
- WebApplicationInitializer 接口
在这个接口中,代码注释还是写的很全面的。xml 方式和 Java 配置的方法都介绍了,还有值得提的是:使用 xml 注册的 servlet 后,仍然可以使用 Java 配置的方式注册另一个 servlet。可以使用org.springframework.core.annotation.Order注解或者实现org.springframework.core.Ordered接口来保证调用的顺序。
这个接口只定义了一个接口:1
2
3
4
5public interface WebApplicationInitializer {
void onStartup(ServletContext servletContext) throws ServletException;
}
servletContext 可以配置任何的 servlets, filters, listeners, context-params, attributes 来提供 Web 应用初始化必须的参数。
AbstractContextLoaderInitializer 抽象类
声明了抽象方法createRootApplicationContext()注册RoogConfig.class配置类中声明的 beanAbstractDispatcherServletInitializer 抽象类
声明了抽象方法registerDispatcherServlet()注册ServletConfig.class配置类中声明的 bean
然后就发现,好像没了。并没有像解析 XML 或者注册 bean 那样通过接口或者其他的代理对我们配置文件里面的 bean 进行解析。
SpringServletContainerInitializer
这个是 Spring 提供的 javax.servlet.ServletContainerInitializer 接口的实现类。在 Servlet3.0 的容器中会自动被识别配置为 Servlet 容器。 正如开篇所言这个类会调用 org.springframework.web.servlet.support.AbstractDispatcherServletInitializer#onStartup 方法。
注册启动 onStartup
在方法 org.springframework.web.context.AbstractContextLoaderInitializer#onStartup() 中注册了 ContextLoaderListener 对象。ContextLoaderListener 对象是 SerlvetContextListener 的实现类。容器 ServletContext 启动之后就会调用 contextInitialized 方法。先注册 ContextLoaderListener 然后再注册 DispatcherServlet,代码如下:1
2
3
4
5
6//org.springframework.web.servlet.support.AbstractDispatcherServletInitializer#onStartup
public void onStartup(ServletContext servletContext) throws ServletException {
super.onStartup(servletContext); // 调用父类方法注册 ContextLoaderListener
registerDispatcherServlet(servletContext); // 注册 DispatcherServlet
}
ContextLoaderListener
这里添加的时 createRootApplicationContext 创建 WebApplicationContext,如果创建 DispatcherServlet 的时候则是条用 org.springframework.web.servlet.support.AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer() 方法。1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14protected void registerContextLoaderListener(ServletContext servletContext) {
// 创建了 AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext 对象
WebApplicationContext rootAppContext = createRootApplicationContext();
if (rootAppContext != null) {
// 添加到 ContextLoaderListener 的 this.context 中
ContextLoaderListener listener = new ContextLoaderListener(rootAppContext);
listener.setContextInitializers(getRootApplicationContextInitializers());
servletContext.addListener(listener);
}
else {
logger.debug("No ContextLoaderListener registered, as " +
"createRootApplicationContext() did not return an application context");
}
}
上述方法添加了一个 AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext 对象到 ContextLoaderLister 中。文档中说:对于多个 @Configuration 注解配置类,后面的 @Bean 定义将复写前面的定义。在上面的方法中,createRootApplicationContext() 方法有必要再看一下:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13 // org.springframework.web.servlet.support.AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer#createRootApplicationContext
protected WebApplicationContext createRootApplicationContext() {
Class<?>[] configClasses = getRootConfigClasses();
if (!ObjectUtils.isEmpty(configClasses)) {
AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext rootAppContext = new AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext();
rootAppContext.register(configClasses);
return rootAppContext;
}
else {
return null;
}
}
getRootConfigClasses() 方法在自定义的 SpringMvcInitializer 类中被实现,并返回 RootConfig.class 配置类。这里可以看出 getRootConfigClasses() 方法返回的类中标识过 @Configuration 注解的类,会通过 ContextLoaderListener 初始化到 ServletContext 中。
WebApplicationContext
由于 ContextLoaderListener 接口实现了 ServletContextListener 接口,所以在所有 Filter 和 Servlet 被初始化之前会通知 ServletContextListener 的 contextInitialized() 方法。1
2
3
4
5
public void contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent event) {
// event.getServletContext() 方法返回 ContextLoaderListener 创建时添加的 AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext
initWebApplicationContext(event.getServletContext());
}
此处也是委托给 org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoader#initWebApplicationContext 方法,方法中有一行代码:servletContext.setAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, this.context); 把初始化过的 applicationContext 添加到 servletContext 中。这里有一个疑问:事务处理失效的问题(先摆在这里)。
DispatcherServlet
然后是把 getServletConfigClasses() 方法中标识过 @Configuration 注解的类,注册到 WebApplicationContext 后,由 DispatcherServlet 添加到 javax.servlet.ServletRegistration.Dynamic。
- 见代码如下:
1 | // 添加配置类到 WebApplicationContext |
通过观察 servletAppContext 与 rootAppContext 的创建过程,区别:
- 返回的配置类不同
和后续的处理方式不同 rootAppContext 时添加到 ContextLoaderListener 后把 listener 加入 servletContext,servletAppContext 封装成 dispatcherServlet 后添加到 servletContext,这里 DispatcherServlet 也是一个 Servlet,在容器启动的时候就会执行相应的
init()方法。- DispatcherServlet 类图:
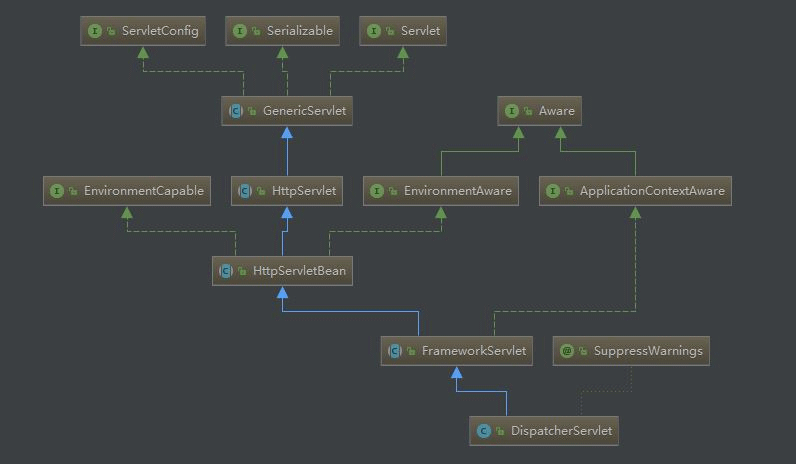
这里再梳理一下,启动的时候 Servlet 容器会找到javax.servlet.ServletContainerInitializer的实现类 SpringServletContainerInitializer,这个接口通过类注解@HandlesTypes(WebApplicationInitializer.class)找到 WebApplicationInitializer。然后开始初始化,跟踪代码发得知,HttpServlet 与 GenericServlet 的 init() 方法并没有对容器作初始化操作。实质的操作在org.springframework.web.servlet.FrameworkServlet#initServletBean()方法。 其核心代码如下:1
2
3
4
5
6try{
this.webApplicationContext = initWebApplicationContext();
initFrameworkServlet();
}catch(Exceltion e){
// ...
}
- DispatcherServlet 类图:
WebApplicationContext 初始化
WebApplicationContext 是在创建 ContextLoaderListener 时创建的 AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext 对象。这里对其进一步初始化操作,代码就不贴出来了,参看方法 org.springframework.web.servlet.FrameworkServlet#initWebApplicationContext。首先通过1
2WebApplicationContext rootContext =
WebApplicationContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(getServletContext());
取出已经创建好的 webApplicationContext,initWebApplicationContext() 方法中 this.webApplicationContext 不会为空,因为在注册 dispatcherServlet 的时候已经放入了 servletAppContext 对象。初始化会调用 configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext() 进行上下文的配置刷新。
FrameworkServlet 类中的 onRefresh() 方法,在子类 DispatcherServlet 中被实现,其也是调用 initStrategies() 方法。都是进行一些必要的初始化操作,详情如下:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11protected void initStrategies(ApplicationContext context) {
initMultipartResolver(context);
initLocaleResolver(context);
initThemeResolver(context);
initHandlerMappings(context);
initHandlerAdapters(context);
initHandlerExceptionResolvers(context);
initRequestToViewNameTranslator(context);
initViewResolvers(context);
initFlashMapManager(context);
}
HandlerMapping
当发生 request 时 DispatcherServlet 会把请求交给 HandlerMapping,HandlerMapping 根据 WebApplicationContext 的配置回传给 DispatcherServlet 相应的 Controller。1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31private void initHandlerMappings(ApplicationContext context) {
this.handlerMappings = null;
if (this.detectAllHandlerMappings) {
// Find all HandlerMappings in the ApplicationContext, including ancestor contexts.
Map<String, HandlerMapping> matchingBeans =
BeanFactoryUtils.beansOfTypeIncludingAncestors(context, HandlerMapping.class, true, false);
if (!matchingBeans.isEmpty()) {
this.handlerMappings = new ArrayList<HandlerMapping>(matchingBeans.values());
// We keep HandlerMappings in sorted order.
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(this.handlerMappings);
}
}
else {
try {
HandlerMapping hm = context.getBean(HANDLER_MAPPING_BEAN_NAME, HandlerMapping.class);
this.handlerMappings = Collections.singletonList(hm);
}
catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex) {
// Ignore, we'll add a default HandlerMapping later.
}
}
// Ensure we have at least one HandlerMapping, by registering
// a default HandlerMapping if no other mappings are found.
if (this.handlerMappings == null) {
this.handlerMappings = getDefaultStrategies(context, HandlerMapping.class);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("No HandlerMappings found in servlet '" + getServletName() + "': using default");
}
}
}
可以看出 HandlerMapping 可以有多个且 this.detectAllHandlerMappings 默认值为 true,也就是默认发现所有实现了 HandlerMapping 的 bean。可以通过复写 org.springframework.web.servlet.support.AbstractDispatcherServletInitializer#customizeRegistration() 来实现初始值的设置。在这个方法中还可以设置文件临时目录、大小等,实例如下:1
2
3
4
5
6
protected void customizeRegistration(ServletRegistration.Dynamic registration) {
MultipartConfigElement multipartConfigElement = new MultipartConfigElement("/tmp/uploads", 2 * 1024 * 1024, 4 * 1024 * 1024, 0);
registration.setInitParameter("detectAllHandlerMappings", "false");
registration.setMultipartConfig(multipartConfigElement);
}
如果没有找到定义的 handlerMapping 则会根据 DispatcherServlet 类目录下的 DispatcherServlet.properties 的定义创建。getDefaultStrategies() 方法通过读取 defaultStrategies 属性来创建 handlerMapping。defaultStrategies 则由以下代码初始化:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12static {
// Load default strategy implementations from properties file.
// This is currently strictly internal and not meant to be customized
// by application developers.
try {
ClassPathResource resource = new ClassPathResource(DEFAULT_STRATEGIES_PATH, DispatcherServlet.class);
defaultStrategies = PropertiesLoaderUtils.loadProperties(resource);
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Could not load '" + DEFAULT_STRATEGIES_PATH + "': " + ex.getMessage());
}
}
常量:DEFAULT_STRATEGIES_PATH 的值为:DispatcherServlet.properties。
- 加载 properties 文件
ClassPathResource 构造器传入属性文件名和类,属性加载时通过工具类PropertiesLoaderUtils完成,大体过程如下:
PropertiesLoaderUtils.loadProperties
1
2
3
4
5public static Properties loadProperties(Resource resource) throws IOException {
Properties props = new Properties();
fillProperties(props, resource);
return props;
}fillProperties
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15public static void fillProperties(Properties props, Resource resource) throws IOException {
InputStream is = resource.getInputStream();
try {
String filename = resource.getFilename();
if (filename != null && filename.endsWith(XML_FILE_EXTENSION)) { // 常量 XML_FILE_EXTENSION = ".xml"
props.loadFromXML(is);
}
else {
props.load(is);
}
}
finally {
is.close();
}
}
HandlerAdapter
很明显,这是一个典型的适配器模式。其初始化逻辑跟 HandlerMapping 类似,默认情况下还是从 DispatcherServlet.properties 文件中加载。
HTTP 请求处理适配器:HttpRequestHandlerAdapter
仅仅支持对 HTTP 请求处理器的适配。简单的将 HTTP 请求对象和响应对象传递给 HTTP 请求处理器的实现,不需求要返回值,主要用在基于 HTTP 的远程调用上。1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12public interface HttpRequestHandler {
/**
* Process the given request, generating a response.
* @param request current HTTP request
* @param response current HTTP response
* @throws ServletException in case of general errors
* @throws IOException in case of I/O errors
*/
void handleRequest(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException;
}简单控制器处理适配器:SimpleControllerHandlerAdapter
实现将 HTTP 请求适配到一个控制器的实现进行处理。注解方法处理器适配器:AnnotationMethodHandlerAdapter
它需要结合注解映射和注解方法处理器协同工作。通过解析声明在出街控制器的请求映射信息来解析相应的处理器方法来处理当前的 HTTP 请求。
HandlerExceptionResolver
初始化过程和 HandlerMapping。基于 HandlerExceptionResolver 的异常解析,Spring 会搜索所有实现了 HandlerExceptionResolver 接口并注册在环境中的 bean,挨个执行,直到返回一个 ModelAndView 对象。
1 | public class ExceptionHandler implements HandlerExceptionResolver { |
RequestToViewNameTranslator
To be continue
DispatcherServlet 处理逻辑
To be continue
